- Available for: Scala 2.13.x, 3.3.x and later
- Auto loading of missing values
- Expiry of not used records
- Deleting oldest values in case of exceeding max size
- Tagless Final
- Partition entries by
hashCodeinto multiple caches in order to avoid thread contention for some corner cases
Cache is a main entry point towards scache library. Most users may want to
call Cache#expiring method to get the instance of the trait. The
documentation could be found in source code of
Cache.scala and also at
javadoc.io.
See Setup for more details on how to add the library itself.
trait Cache[F[_], K, V] {
def get(key: K): F[Option[V]]
def getOrElse(key: K, default: => F[V]): F[V]
/**
* Does not run `value` concurrently for the same key
*/
def getOrUpdate(key: K)(value: => F[V]): F[V]
/**
* Does not run `value` concurrently for the same key
* Releasable.release will be called upon key removal from the cache
*/
def getOrUpdateReleasable(key: K)(value: => F[Releasable[F, V]]): F[V]
/**
* @return previous value if any, possibly not yet loaded
*/
def put(key: K, value: V): F[F[Option[V]]]
def put(key: K, value: V, release: F[Unit]): F[F[Option[V]]]
def size: F[Int]
def keys: F[Set[K]]
/**
* Might be an expensive call
*/
def values: F[Map[K, F[V]]]
/**
* @return previous value if any, possibly not yet loaded
*/
def remove(key: K): F[F[Option[V]]]
/**
* Removes loading values from the cache, however does not cancel them
*/
def clear: F[F[Unit]]
}trait SerialMap[F[_], K, V] {
def get(key: K): F[Option[V]]
def getOrElse(key: K, default: => F[V]): F[V]
/**
* Does not run `value` concurrently for the same key
*/
def getOrUpdate(key: K, value: => F[V]): F[V]
def put(key: K, value: V): F[Option[V]]
/**
* `f` will be run serially for the same key, entry will be removed in case of `f` returns `none`
*/
def modify[A](key: K)(f: Option[V] => F[(Option[V], A)]): F[A]
/**
* `f` will be run serially for the same key, entry will be removed in case of `f` returns `none`
*/
def update[A](key: K)(f: Option[V] => F[Option[V]]): F[Unit]
def size: F[Int]
def keys: F[Set[K]]
/**
* Might be an expensive call
*/
def values: F[Map[K, V]]
def remove(key: K): F[Option[V]]
def clear: F[Unit]
}scache, along with its dependencies, is available on Evolution's JFrog Artifactory. That is why one needs to include
a dependency on https://github.com/evolution-gaming/sbt-artifactory-plugin.
addSbtPlugin("com.evolution" % "sbt-artifactory-plugin" % "0.0.2")
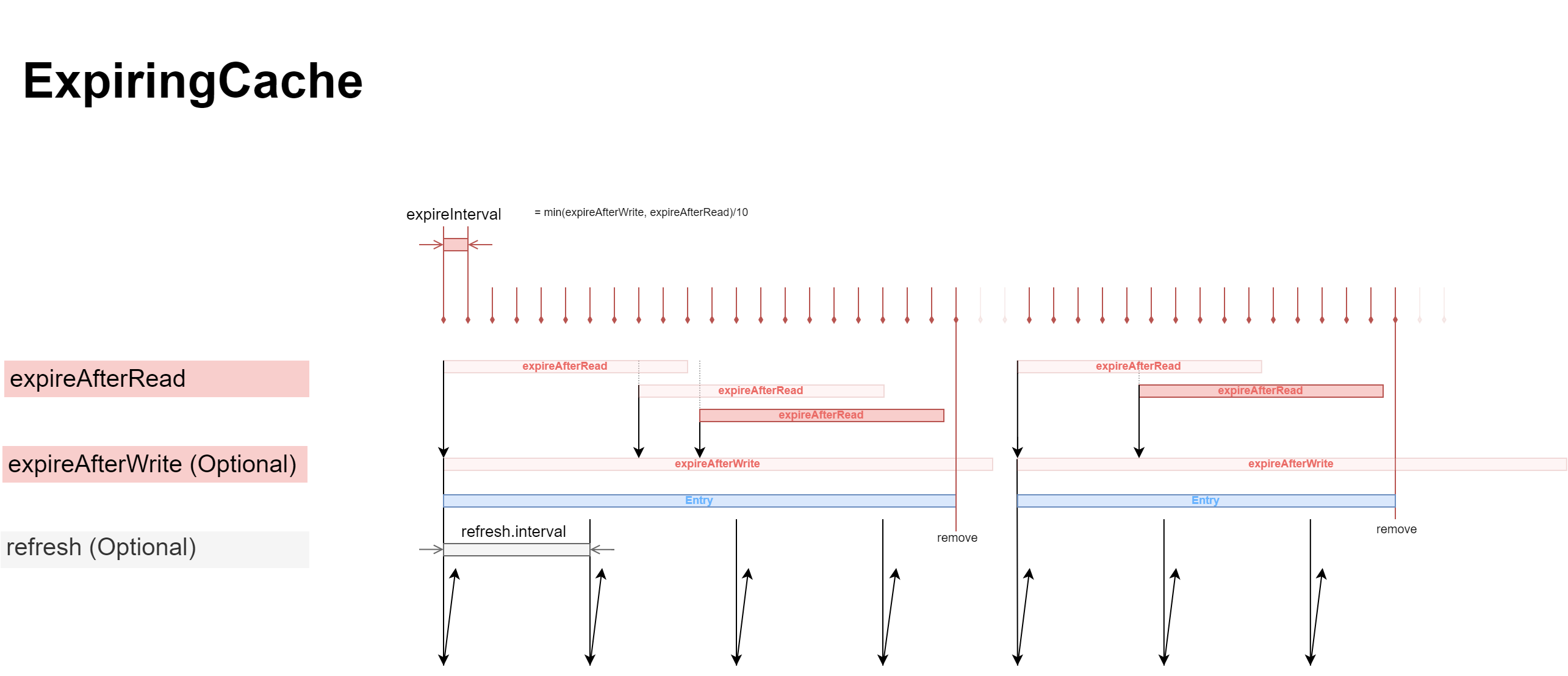
libraryDependencies += "com.evolution" %% "scache" % "<latest version from badge>"- There is no use to make refresh.interval bigger than expireAfterWrite. It's just the waste of resources.
- Touch, despite its name, is not called after refresh.
- expireAfterWrite, despite its name, is calculated from date of creation, not time of update.
The release process is based on Git tags and makes use of evolution-gaming/scala-github-actions which uses sbt-dynver to automatically obtain the version from the latest Git tag. The flow is defined in .github/workflows/release.yml.
A typical release process is as follows:
- Create and push a new Git tag. The version should be in the format
vX.Y.Z(example:v4.1.0). Example:git tag v4.1.0 && git push origin v4.1.0 - On success, a new GitHub release is automatically created with a calculated diff and auto-generated release notes. You can see it on
Releasespage, change the description if needed - On failure, the tag is deleted from the remote repository. Please note that your local tag isn't deleted, so if the failure is recoverable then you can delete the local tag and try again (an example of unrecoverable failure is successfully publishing only a few of the artifacts to Artifactory which means a new attempt would fail since Artifactory doesn't allow overwriting its contents)