Introduction
This tutorial teaches you GitHub essentials like repositories, branches, commits, and pull requests. You'll create your own Hello World repository and learn GitHub's pull request workflow, a popular way to create and review code.
In this quickstart guide, you will:
- Create and use a repository.
- Start and manage a new branch.
- Make changes to a file and push them to GitHub as commits.
- Open and merge a pull request.
Prerequisites
-
You must have a GitHub account. For more information, see Creating an account on GitHub.
-
You don't need to know how to code, use the command line, or install Git (the version control software that GitHub is built on).
Step 1: Create a repository
The first thing we'll do is create a repository. You can think of a repository as a folder that contains related items, such as files, images, videos, or even other folders. A repository usually groups together items that belong to the same "project" or thing you're working on.
Often, repositories include a README file, a file with information about your project. README files are written in Markdown, which is an easy-to-read, easy-to-write language for formatting plain text. We'll learn more about Markdown in the next tutorial, Setting up your profile.
GitHub lets you add a README file at the same time you create your new repository. GitHub also offers other common options such as a license file, but you do not have to select any of them now.
Your hello-world repository can be a place where you store ideas, resources, or even share and discuss things with others.
-
In the upper-right corner of any page, select , then click New repository.
-
In the "Repository name" box, type
hello-world. -
In the "Description" box, type a short description. For example, type "This repository is for practicing the GitHub Flow."
-
Select whether your repository will be Public or Private.
-
Select Add a README file.
-
Click Create repository.
Step 2: Create a branch
Branching lets you have different versions of a repository at one time.
By default, your repository has one branch named main that is considered to be the definitive branch. You can create additional branches off of main in your repository.
Branching is helpful when you want to add new features to a project without changing the main source of code. The work done on different branches will not show up on the main branch until you merge it, which we will cover later in this guide. You can use branches to experiment and make edits before committing them to main.
When you create a branch off the main branch, you're making a copy, or snapshot, of main as it was at that point in time. If someone else made changes to the main branch while you were working on your branch, you could pull in those updates.
This diagram shows:
- The
mainbranch - A new branch called
feature - The journey that
featuretakes through stages for "Commit changes," "Submit pull request," and "Discuss proposed changes" before it's merged intomain
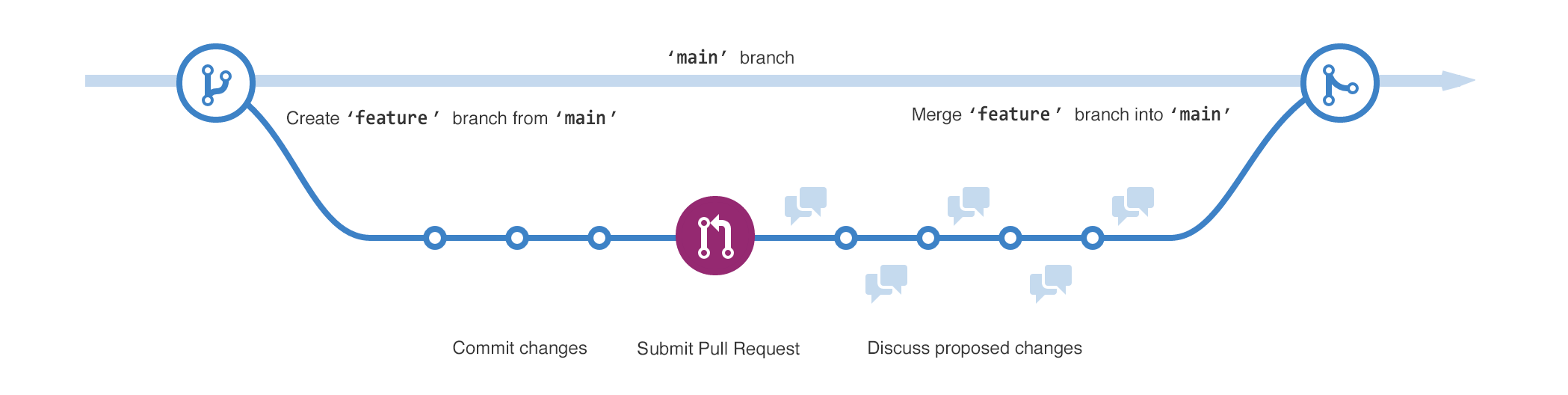
Creating a branch
-
Click the Code tab of your
hello-worldrepository. -
Above the file list, click the dropdown menu that says main.
-
Type a branch name,
readme-edits, into the text box. -
Click Create branch: readme-edits from main.
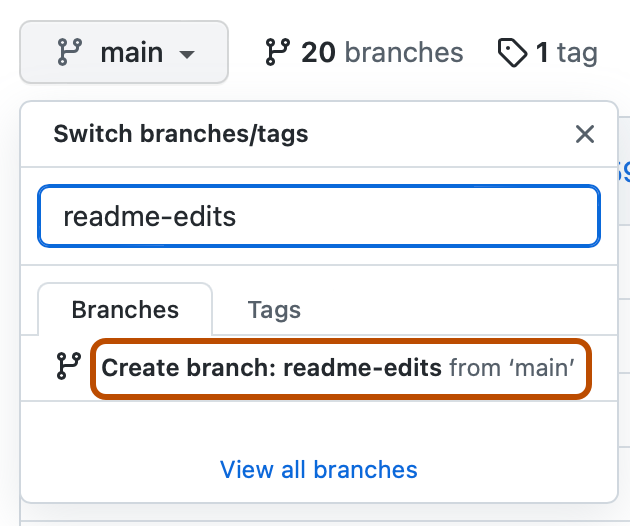
Now you have two branches, main and readme-edits. Right now, they look exactly the same. Next you'll add changes to the new readme-edits branch.
Step 3: Make and commit changes
When you created a new branch in the previous step, GitHub brought you to the code page for your new readme-edits branch, which is a copy of main.
You can make and save changes to the files in your repository. On GitHub, saved changes are called commits. Each commit has an associated commit message, which is a description explaining why a particular change was made. Commit messages capture the history of your changes so that other contributors can understand what you’ve done and why.
- Under the
readme-editsbranch you created, click theREADME.mdfile. - To edit the file, click .
- In the editor, write a bit about yourself.
- Click Commit changes.
- In the "Commit changes" box, write a commit message that describes your changes.
- Click Commit changes.
These changes will be made only to the README file on your readme-edits branch, so now this branch contains content that's different from main.
Step 4: Open a pull request
Now that you have changes in a branch off of main, you can open a pull request.
Pull requests are the heart of collaboration on GitHub. When you open a pull request, you're proposing your changes and requesting that someone review and pull in your contribution and merge them into their branch. Pull requests show diffs, or differences, of the content from both branches. The changes, additions, and subtractions are shown in different colors.
As soon as you make a commit, you can open a pull request and start a discussion, even before the code is finished.
In this step, you'll open a pull request in your own repository and then merge it yourself. It's a great way to practice the GitHub flow before working on larger projects.
-
Click the Pull requests tab of your
hello-worldrepository. -
Click New pull request.
-
In the Example Comparisons box, select the branch you made,
readme-edits, to compare withmain(the original). -
Look over your changes in the diffs on the Compare page, make sure they're what you want to submit.
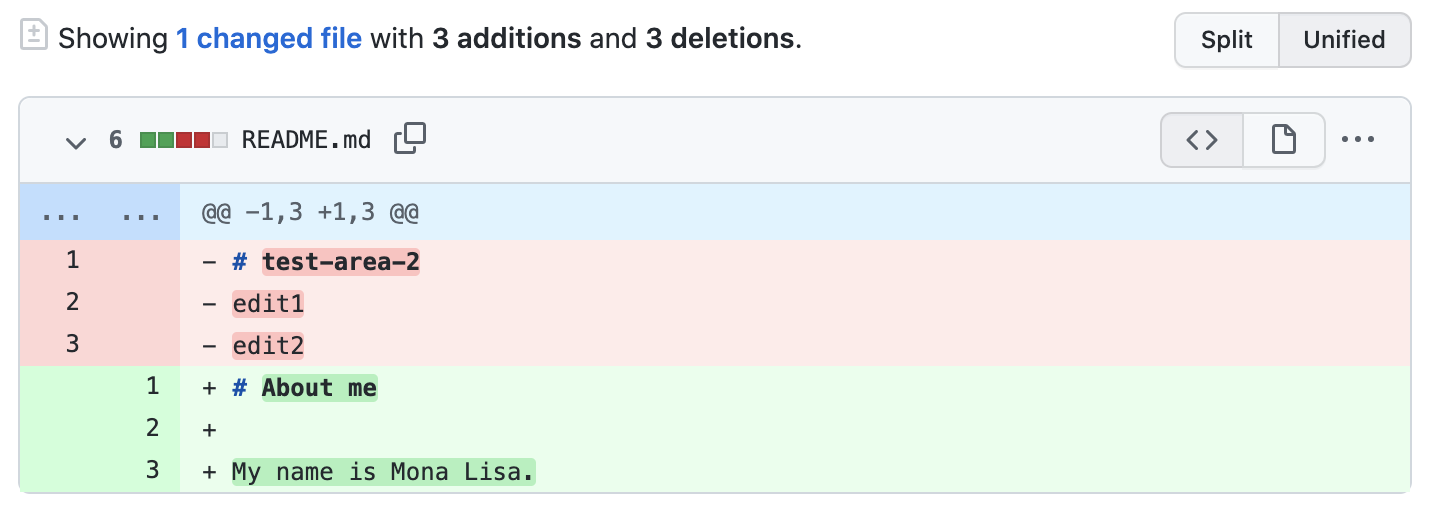
-
Click Create pull request.
-
Give your pull request a title and write a brief description of your changes. You can include emojis and drag and drop images and gifs.
-
Click Create pull request.
Reviewing a pull request
When you start collaborating with others, this is the time you'd ask for their review. This allows your collaborators to comment on, or propose changes to, your pull request before you merge the changes into the main branch.
We won't cover reviewing pull requests in this tutorial, but if you're interested in learning more, see About pull request reviews. Alternatively, try the GitHub Skills "Reviewing pull requests" course.
Step 5: Merge your pull request
In this final step, you will merge your readme-edits branch into the main branch. After you merge your pull request, the changes on your readme-edits branch will be incorporated into main.
Sometimes, a pull request may introduce changes to code that conflict with the existing code on main. If there are any conflicts, GitHub will alert you about the conflicting code and prevent merging until the conflicts are resolved. You can make a commit that resolves the conflicts or use comments in the pull request to discuss the conflicts with your team members.
In this walk-through, you should not have any conflicts, so you are ready to merge your branch into the main branch.
- At the bottom of the pull request, click Merge pull request to merge the changes into
main. - Click Confirm merge. You will receive a message that the request was successfully merged and the request was closed.
- Click Delete branch. Now that your pull request is merged and your changes are on
main, you can safely delete thereadme-editsbranch. If you want to make more changes to your project, you can always create a new branch and repeat this process. - Click back to the Code tab of your
hello-worldrepository to see your published changes onmain.
Conclusion
By completing this tutorial, you've learned to create a project and make a pull request on GitHub.
As part of that, we've learned how to:
- Create a repository.
- Start and manage a new branch.
- Change a file and commit those changes to GitHub.
- Open and merge a pull request.
Next steps
- Take a look at your GitHub profile and you'll see your work reflected on your contribution graph.
- If you want to practice the skills you've learned in this tutorial again, try the GitHub Skills "Introduction to GitHub" course.
- In the next tutorial, Setting up your profile, you'll learn how to personalize your profile and you'll also learn some basic Markdown syntax for writing on GitHub.