Monitoring your workflows
Monitoring your current jobs in your organization or enterprise
To identify any constraints with concurrency or queuing, you can check how many jobs are currently being processed on the GitHub-hosted runners in your organization or enterprise. For more information, see Monitoring your current jobs.
Using the visualization graph
Every workflow run generates a real-time graph that illustrates the run progress. You can use this graph to monitor and debug workflows. For example:
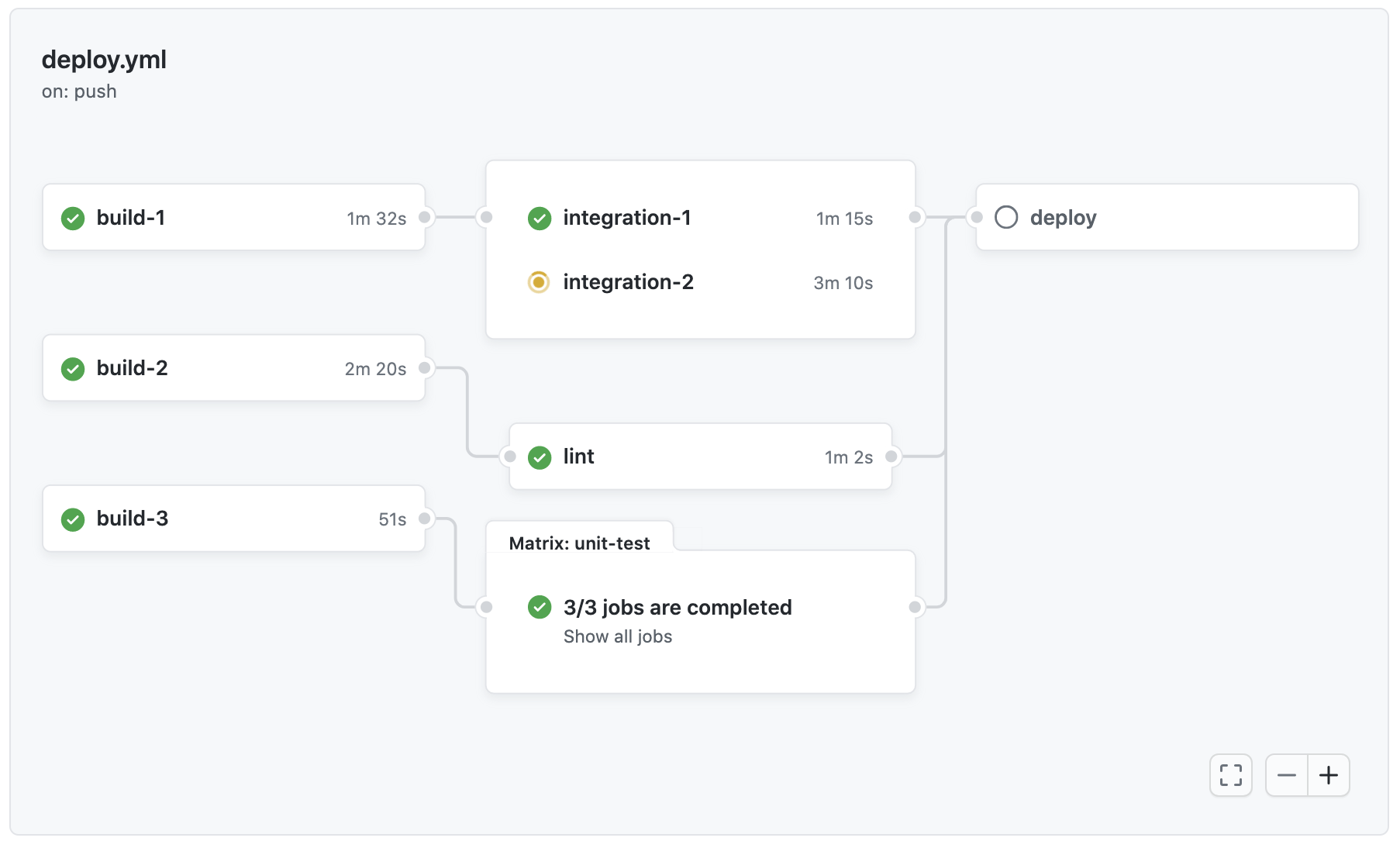
For more information, see Using the visualization graph.
Adding a workflow status badge
A status badge shows whether a workflow is currently failing or passing. A common place to add a status badge is in the README.md file of your repository, but you can add it to any web page you'd like. By default, badges display the status of your default branch. If there are no workflow runs on your default branch, it will display the status of the most recent run across all branches. You can display the status of a workflow run for a specific branch or event using the branch and event query parameters in the URL.

For more information, see Adding a workflow status badge.
Viewing job execution time
To identify how long a job took to run, you can view its execution time. For more information, see Viewing job execution time.
Viewing workflow run history
You can view the status of each job and step in a workflow. For more information, see Viewing workflow run history.
Monitoring GitHub Actions metrics
To analyze the efficiency and reliability of your workflows using metrics, see Viewing GitHub Actions metrics.
Monitoring self-hosted runners
If you use self-hosted runners, you can view their activity and diagnose common issues.
For more information, see Monitoring and troubleshooting self-hosted runners.