| title | intro | permissions | redirect_from | versions | topics | shortTitle | type | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Creating an issue |
Issues can be created in a variety of ways, so you can choose the most convenient method for your workflow. |
People with read access can create an issue in a repository where issues are enabled. {% data reusables.enterprise-accounts.emu-permission-repo %} |
|
|
|
Create an issue |
how_to |
Issues can be used to keep track of bugs, enhancements, or other requests. For more information, see AUTOTITLE.
{% data reusables.repositories.administrators-can-disable-issues %}
{% data reusables.repositories.navigate-to-repo %} {% data reusables.repositories.sidebar-issues %} {% data reusables.repositories.new_issue %}
-
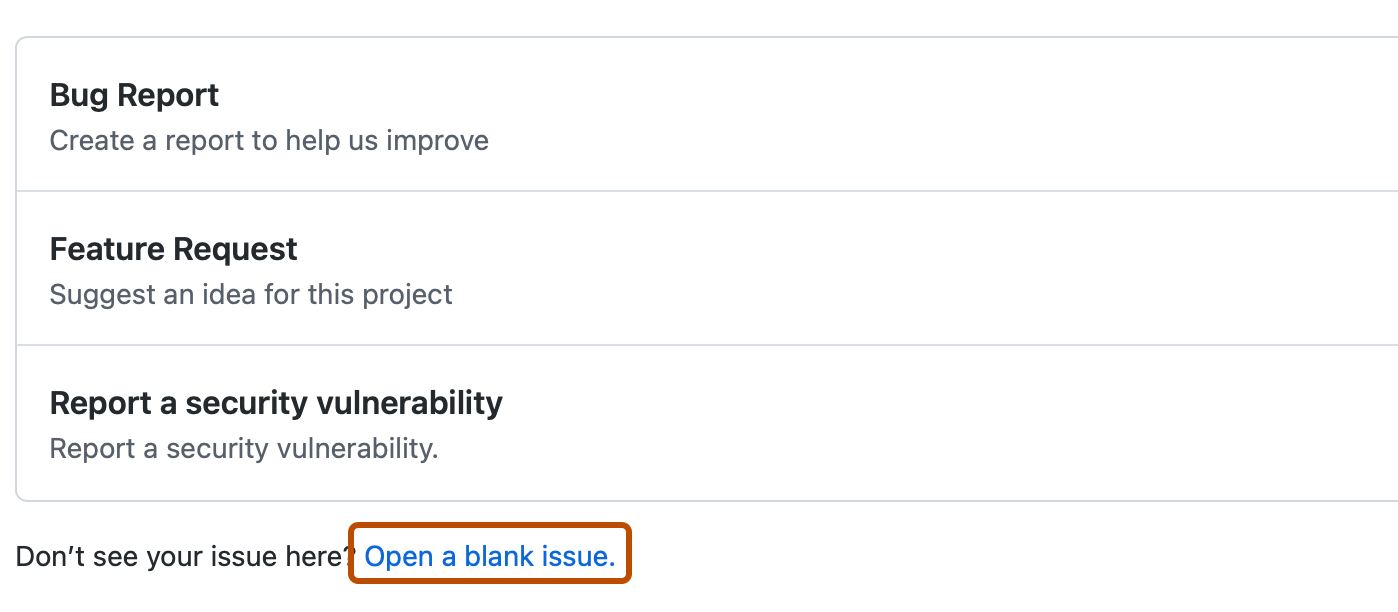
If your repository uses issue templates, next to the type of issue you'd like to open, click Get started.
If the type of issue you'd like to open isn't included in the available options, click Open a blank issue.
 {% data reusables.repositories.type-issue-title-and-description %}
{% data reusables.repositories.assign-an-issue-as-project-maintainer %}
{% data reusables.repositories.submit-new-issue %}
{% data reusables.repositories.type-issue-title-and-description %}
{% data reusables.repositories.assign-an-issue-as-project-maintainer %}
{% data reusables.repositories.submit-new-issue %}
{% data reusables.cli.about-cli %} To learn more about {% data variables.product.prodname_cli %}, see AUTOTITLE.
To create an issue, use the gh issue create subcommand. To skip the interactive prompts, include the --body and the --title flags.
gh issue create --title "My new issue" --body "Here are more details."You can also specify assignees, labels, milestones, and projects.
gh issue create --title "My new issue" --body "Here are more details." --assignee @me,monalisa --label "bug,help wanted" --project onboarding --milestone "learning codebase"You can open a new issue from a comment in an issue or pull request. When you open an issue from a comment, the issue contains a snippet showing where the comment was originally posted.
-
Navigate to the comment that you would like to open an issue from.
-
In that comment, click {% octicon "kebab-horizontal" aria-label="Show options" %}.
-
Click Reference in new issue.
-
Use the "Repository" dropdown menu, and select the repository you want to open the issue in.
-
Type a descriptive title and body for the issue.
-
Click Create issue. {% data reusables.repositories.assign-an-issue-as-project-maintainer %} {% data reusables.repositories.submit-new-issue %}
You can open a new issue from a specific line or lines of code in a file or pull request. When you open an issue from code, the issue contains a snippet showing the line or range of code you chose. You can only open an issue in the same repository where the code is stored.
{% data reusables.repositories.navigate-to-repo %}
-
Locate the code you want to reference in an issue:
- To open an issue about code in a file, navigate to the file.
- To open an issue about code in a pull request, navigate to the pull request and click {% octicon "diff" aria-hidden="true" %} Files changed. Then, browse to the file that contains the code you want included in your comment, and click View. {% data reusables.repositories.choose-line-or-range %}
-
To the left of the code range, click {% octicon "kebab-horizontal" aria-label="Code line X options" %}. In the dropdown menu, click Reference in new issue.
 {% data reusables.repositories.type-issue-title-and-description %}
{% data reusables.repositories.assign-an-issue-as-project-maintainer %}
{% data reusables.repositories.submit-new-issue %}
{% data reusables.repositories.type-issue-title-and-description %}
{% data reusables.repositories.assign-an-issue-as-project-maintainer %}
{% data reusables.repositories.submit-new-issue %}
People with triage permission to a repository can create an issue from a discussion.
When you create an issue from a discussion, the contents of the discussion post will be automatically included in the issue body, and any labels will be retained. Creating an issue from a discussion does not convert the discussion to an issue or delete the existing discussion. For more information about {% data variables.product.prodname_discussions %}, see AUTOTITLE.
{% data reusables.discussions.discussions-tab %} {% data reusables.discussions.click-discussion-in-list %}
-
In the right sidebar, click {% octicon "issue-opened" aria-hidden="true" %} Create issue from discussion.
{% data reusables.repositories.type-issue-title-and-description %} {% data reusables.repositories.assign-an-issue-as-project-maintainer %} {% data reusables.repositories.submit-new-issue %}
{% data reusables.projects.about-issue-modal %} For more information about Projects, see AUTOTITLE.
- Navigate to your project. {% data reusables.projects.create-issue-modal %}
{% ifversion projects-v1 %}
If you're using a {% data variables.projects.projects_v1_board %} to track and prioritize your work, you can convert notes to issues. For more information, see AUTOTITLE and AUTOTITLE.
{% endif %}
{% ifversion fpt or ghec %}
Within an issue, you can use task lists to break work into smaller tasks and track the full set of work to completion. If a task requires further tracking or discussion, you can convert the task to an issue by hovering over the task and clicking {% octicon "issue-opened" aria-label="The issue opened icon" %} in the upper-right corner of the task. For more information, see AUTOTITLE.
{% endif %}
You can use query parameters to open issues. Query parameters are optional parts of a URL you can customize to share a specific web page view, such as search filter results or an issue template on {% data variables.product.prodname_dotcom %}. To create your own query parameters, you must match the key and value pair.
Tip
You can also create issue templates that open with default labels, assignees, and an issue title. For more information, see AUTOTITLE.
You must have the proper permissions for any action to use the equivalent query parameter. For example, you must have permission to add a label to an issue to use the labels query parameter. For more information, see AUTOTITLE.
If you create an invalid URL using query parameters, or if you don’t have the proper permissions, the URL will return a 404 Not Found error page. If you create a URL that exceeds the server limit, the URL will return a 414 URI Too Long error page.
| Query parameter | Example |
|---|---|
title |
https://github.com/octo-org/octo-repo/issues/new?labels=bug&title=New+bug+report creates an issue with the label "bug" and title "New bug report." |
body |
https://github.com/octo-org/octo-repo/issues/new?title=New+bug+report&body=Describe+the+problem. creates an issue with the title "New bug report" and the comment "Describe the problem" in the issue body. |
labels |
https://github.com/octo-org/octo-repo/issues/new?labels=help+wanted,bug creates an issue with the labels "help wanted" and "bug". |
milestone |
https://github.com/octo-org/octo-repo/issues/new?milestone=testing+milestones creates an issue with the milestone "testing milestones." |
assignees |
https://github.com/octo-org/octo-repo/issues/new?assignees=octocat creates an issue and assigns it to @octocat. |
projects |
https://github.com/octo-org/octo-repo/issues/new?title=Bug+fix&projects=octo-org/1 creates an issue with the title "Bug fix" and adds it to the organization's project 1. {% ifversion projects-v2 and projects-v1 %}{% ifversion projects-in-issue-forms %}{% else %}Only {% data variables.projects.projects_v1_boards %} can currently be specified in URL queries.{% endif %}{% endif %} |
template |
https://github.com/octo-org/octo-repo/issues/new?template=issue_template.md creates an issue with a template in the issue body. The template query parameter works with templates stored in an ISSUE_TEMPLATE subdirectory within the root, docs/ or .github/ directory in a repository. For more information, see AUTOTITLE. |
{% ifversion fpt or ghec %} You can also use URL query parameters to fill custom text fields that you have defined in issue form templates. Query parameters for issue form fields can also be passed to the issue template chooser. For more information, see AUTOTITLE. {% endif %}
{% ifversion code-scanning-task-lists %}
{% data reusables.code-scanning.beta-alert-tracking-in-issues %} If you're using issues to track and prioritize your work, you can use issues to track {% data variables.product.prodname_code_scanning %} alerts. {% data reusables.code-scanning.alert-tracking-link %}
{% endif %}